- Data integrity
- validity and accuracy of data, maintain health of database
- 3 constraints of data model: entity integrity[tables, columns, rows, primary key], referential integrity[foreign key] and domain integrity[ways to input data]
SQL vs. Mysql
SQL is structured query language
Mysql is a RDMS, system softwareJOIN
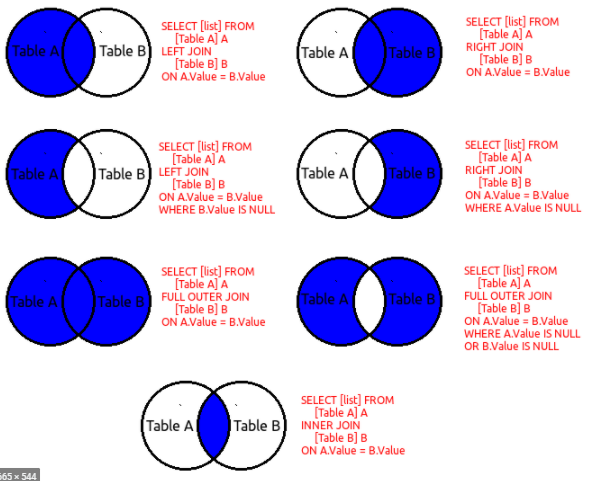
- Join is to combine records(rows) of two or more tables based on related fields(columns)
- 4 types:
- (INNER) JOIN
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN
- SELF-JOIN: join iteself uses inner join or left join
- CROSS-JOIN: cartesian product of two tables included in join
Query
Query is request for data from db, can be either select query or action query, for example, select …, update …Subquery
It is a query within another query, also called nested query or inner queryQuotes use in sql
- Single quotes delimit a string constant or a date/time constant.
- Double quotes delimit identifiers for alias e.g. table names or column names.
View
It is result set of sql statement, store in tablesCommon clauses
- [HAVING] is to filter records with combination of GROUP BY, different from WHERE,which can not filter aggregated records
- [UNION] combine and return result-sets from two or more select statement, [UNION ALL] include duplicates
- [MINUS] remove result-set from second query
- [INTERSECT] return result-set from intersection of two select statements
- Statements
- [DELETE] delete rows from table, not free space containing table
- [TRUNCATE TABLE] delete all rows, free space
- [DROP TABLE] delete tables, all rows and table structure are droped
- Matching pattern
use [LIKE]
- % wildcard do simple search, match zero or more characters of any type
- search special character, use [ESCAPE], such as LIKE ‘%/%%’ ESCAPE’/‘
- _ wildcard match pattern at specific position
- Check & exception
- [CHECK] constraint applies any column to limit values
- handle exception
BEGIN TRY
END TRY--code which might raise exception
BEGIN CATCH
END CATCH--code to run if error occurs in try block- error function
ERROR_NUMBER(): As the name says, it returns the error number.
ERROR_STATE(): It returns the state number of the error.
ERROR_SEVERITY(): This function returns the severity value of the error.
ERROR_PROCEDURE(): It returns the name of the stored procedure or function in which the error has occurred.
ERROR_LINE(): Returns the line number at which the error has occurred.
ERROR_MESSAGE(): Returns the message about the error.
- error function
Aggregate and Scalar functions
Aggregate functions:
AVG() - Calculates the mean of a collection of values.
COUNT() - Counts the total number of records in a specific table or view.
MIN() - Calculates the minimum of a collection of values.
MAX() - Calculates the maximum of a collection of values.
SUM() - Calculates the sum of a collection of values.
FIRST() - Fetches the first element in a collection of values.
LAST() - Fetches the last element in a collection of values.
Scalar functions:
LEN() - Calculates the total length of the given field (column).
UCASE() - Converts a collection of string values to uppercase characters.
LCASE() - Converts a collection of string values to lowercase characters.
MID() - Extracts substrings from a collection of string values in a table.
CONCAT() - Concatenates two or more strings.
RAND() - Generates a random collection of numbers of given length.
ROUND() - Calculates the round off integer value for a numeric field (or decimal point values).
NOW() - Returns the current data & time.
FORMAT() - Sets the format to display a collection of values.Backups
Several types of backup along with recording transactions
- Full backup: backup all database objects, system tables, and data
- Transaction log backup: records the transactions since the previous backup
- Differential backup: backup since the last full backup
…